3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Control Valve
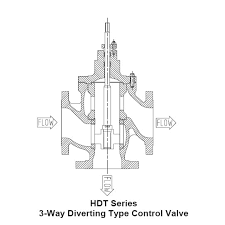
The Application of 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve
Introducing Cameron’s versatile 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve. This valve is essential in various applications, including those requiring precise fluid control like air ride seat control valve, air seat control valve, and air seat height control valve systems. Cameron’s expertise ensures efficient diversion or blending of fluid streams, enhancing performance in pneumatic systems. With robust construction and reliable operation, Cameron’s 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve is a trusted choice for critical air control applications.
What Are The Types Of 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve?
- T-Pattern Valves: These valves have a T-shaped configuration, with one inlet and two outlets or vice versa. They are commonly used for diverting flow from one inlet to two separate outlets or for mixing two inlet streams into one outlet.
- L-Pattern Valves: L-pattern valves have an L-shaped configuration, featuring one inlet and two outlets arranged perpendicular to each other. They are suitable for applications requiring a 90-degree change in flow direction, such as diverting flow around a corner or mixing two streams into one.
- LL-Pattern Valves: LL-pattern valves have two inlets and one outlet arranged in an L-shaped configuration. They are used for diverting flow from two separate inlets into one common outlet.
What Is 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve?
A 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve is a versatile component used in fluid control systems. It redirects or blends fluid streams through its globe-like body, offering dual functionality for diverting or mixing operations. With precise control over flow direction and volume, it efficiently manages fluid distribution in various industrial processes. This valve plays a crucial role in applications requiring flexibility and accuracy in fluid handling, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
How to Select the Right 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve?
To select the right 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve, consider factors like flow rates, pressure ratings, fluid compatibility, and application requirements. Consultation with experts aids optimal selection.
Features of 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve
- Versatility:
- Dual Functionality: Offers both diverting and mixing capabilities in a single valve, reducing the need for multiple valves and simplifying system design.
- Precise Control:
- Fine Adjustment: Allows for precise control over flow rates and direction, ensuring optimal process performance.
- Compact Design:
- Space Saving: Features a compact design, suitable for installations where space is limited, without compromising functionality.
- Durable Construction:
- Robust Materials: Constructed from high-quality materials such as stainless steel or brass, ensuring durability and longevity.
- Leakage Prevention:
- Tight Seal: Provides tight shut-off to prevent leakage and maintain system integrity, enhancing safety and efficiency.
- Easy Maintenance:
- Accessible Components: Designed for easy access to internal components, facilitating maintenance and repair tasks, reducing downtime.
- Adaptable Actuation:
- Manual or Automated Operation: Compatible with manual handwheel operation or automated actuation options like pneumatic or electric actuators, offering flexibility based on application requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve
Advantages:
- Dual Functionality:
- Offers both diverting and mixing capabilities, reducing the need for multiple valves and simplifying system design.
- Versatility:
- Suitable for a wide range of applications, providing flexibility in fluid handling operations.
- Precise Control:
- Allows for precise adjustment of flow rates and direction, ensuring optimal process performance.
- Compact Design:
- Space-saving design suitable for installations where space is limited.
- Durable Construction:
- Constructed from high-quality materials, ensuring durability and longevity.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity:
- More complex design compared to traditional two-way valves, requiring careful consideration during installation and maintenance.
- Cost:
- May have a higher initial cost due to added functionality and complexity of the design.
The Specifications of 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, PVC, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Threaded, Flanged, Welded, etc. |
| Thread Standard | NPT, BSP, BSPT, DIN, etc. |
| Thread Size | 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, or customized |
| Body Material | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Brass, PVC, etc. |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Air, Oil, Chemicals, etc. |
| Handle Type | Lever, Knob, Actuator, etc. |
| Handle Material | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Plastic, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | Up to XXX psi (varies by model) |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | Up to XX bar (varies by model) |
| Operating Pressure | Dependent on system requirements |
The Installation Steps for 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve
- Preparation:
- Gather all necessary tools and equipment, including wrenches, pipe fittings, and thread sealant.
- Ensure the work area is clean and free from debris.
- Valve Inspection:
- Examine the valve for any visible damage or defects.
- Verify that the valve specifications match the requirements of the system.
- Select Location:
- Choose an appropriate location for installing the valve, considering accessibility and operational requirements.
- Ensure sufficient space for maintenance and operation.
- Shut Off System:
- Shut off the flow of fluid to the system where the valve will be installed.
- Release any pressure in the system to prevent accidents during installation.
- Prepare Pipes:
- Clean the pipe ends thoroughly to remove any dirt or debris.
- Apply thread sealant or tape to the male threads of the pipes.
- Mount Valve:
- Position the valve in the desired orientation on the pipeline.
- Use appropriate fittings to secure the valve to the pipeline, ensuring a tight seal.
- Connect Pipes:
- Screw the pipe ends into the valve ports, ensuring proper alignment and tightening to prevent leaks.
- Use a wrench to tighten the connections securely, but avoid over-tightening.
- Test for Leaks:
- Once the valve is installed, pressurize the system and check for any leaks around the valve connections.
- If leaks are detected, tighten the connections further or apply additional sealant as needed.
- Final Checks:
- Confirm that the valve operates smoothly and functions correctly in diverting or mixing fluid streams.
- Label the valve for easy identification and maintenance in the future.
- System Activation:
- Restore the flow of fluid to the system and verify that the valve operates as expected under normal operating conditions.
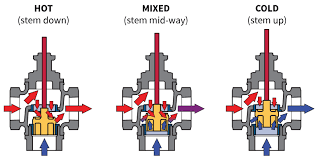
The Operation Theory of 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve
The operation theory of a 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve involves its unique design to redirect or blend fluid streams. By adjusting the position of the internal plug or ball, the valve can control the flow direction and volume, facilitating diverting or mixing operations efficiently.
In comparison, angle seat control valves utilize a piston or diaphragm mechanism to control the flow of fluid through the valve. These valves are often used in applications where precise control of flow rate is necessary, such as in steam and water systems.
Furthermore, the control valve seat plays a critical role in the operation of control valves by providing a sealing surface for the valve plug or ball. The design of the seat influences factors such as flow capacity, leakage rate, and pressure drop across the valve.
Overall, while each type of valve operates on different principles, they all serve the common purpose of controlling fluid flow in industrial processes, with the 3-Way Diverting/Mixing Globe Valve offering specific capabilities for diverting or mixing fluid streams.
