Modulating Control Valve
The Application of Modulating Control Valve
Modulating Control Valves, such as the Rotork Modulating Control Valve, are versatile instruments used in various industries. These valves regulate fluid flow by modulating the position of a closure element based on external signals. They come in different types, including air control valves and hydraulic control valves, each tailored to specific applications. Air control valves manipulate airflow, while hydraulic control valves manage fluid flow in hydraulic systems. With precise modulation capabilities, they ensure accurate control over flow rates, pressures, and temperatures, enhancing process efficiency and system performance. Whether it’s maintaining precise temperatures in HVAC systems or regulating flow rates in industrial processes, Modulating Control Valves play a crucial role in modern engineering systems.
modulation control valve
the modulating control valve is?
What Is Modulating Control Valve?
A Modulating Control Valve is an instrument that adjusts fluid flow by continuously modulating the position of its closure element, ensuring precise control over flow rates, pressures, and temperatures in various applications.
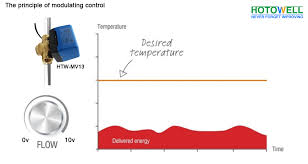
How Does Modulating Control Valve work?
A Modulating Control Valve operates by receiving signals from external controllers, which adjust the valve’s position to regulate fluid flow. This continuous modulation allows for precise control over flow rates, pressures, and temperatures, ensuring optimal performance in diverse industrial processes.
Features of Modulating Control Valve
- Precision Control: Modulating Control Valves offer precise adjustment of flow rates, pressures, and temperatures, ensuring accurate regulation in various applications.
- Versatility: These valves are adaptable to different fluid types, pressures, and temperature ranges, making them suitable for diverse industrial processes.
- Continuous Modulation: They enable continuous modulation of flow by adjusting the valve position based on external signals, ensuring smooth and stable operation.
- Responsive Performance: With quick response times, Modulating Control Valves swiftly react to changes in operating conditions, maintaining optimal system performance.
- Energy Efficiency: By precisely controlling fluid flow, these valves help optimize energy consumption, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
- Reliability: Engineered with durable materials and advanced technologies, Modulating Control Valves offer long-term reliability and minimal maintenance requirements.
Advantages of Modulating Control Valve
- Precise Regulation: Modulating control valves provide accurate adjustment of flow rates, pressures, and temperatures, ensuring optimal process control.
- Improved Efficiency: By continuously modulating flow, these valves help optimize system performance, leading to enhanced energy efficiency and reduced operational costs.
- Flexibility: They are adaptable to a wide range of applications and operating conditions, offering versatility in various industrial processes.
- Responsive: Modulating control valves have quick response times, allowing for rapid adjustments to changing process conditions, ensuring consistent performance.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: Their ability to maintain steady operation at varying flow rates minimizes wear and tear on system components, extending equipment lifespan and reducing maintenance needs.
- Enhanced Safety: With precise control over fluid flow, these valves contribute to improved safety by preventing overpressurization and ensuring stable operation within safe limits.

The Specifications of Modulating Control Valve
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Modulating Control Valve |
| Ball Material | [Material] |
| Attachment Type | [Type] |
| Thread Standard | [Standard] |
| Thread Size | [Size] |
| Body Material | [Material] |
| Safe for Use With | [Fluid or Application] |
| Handle Type | [Type] |
| Handle Material | [Material] |
| Maximum Working Pressure psi | [Value] psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure bar | [Value] bar |
| Operating Pressure | [Range or Value] |
The Parameter of Modulating Control Valve
- Type: Modulating Control Valve
- Ball Material: [Specify material, e.g., stainless steel, brass]
- Attachment Type: [Specify type, e.g., flanged, threaded]
- Thread Standard: [Specify standard, e.g., NPT, BSP]
- Thread Size: [Specify size, e.g., 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch]
- Body Material: [Specify material, e.g., carbon steel, PVC]
- Safe for Use With: [Specify fluid or application, e.g., water, steam]
- Handle Type: [Specify type, e.g., lever, knob]
- Handle Material: [Specify material, e.g., plastic, aluminum]
- Maximum Working Pressure psi: [Specify maximum pressure in psi]
- Maximum Working Pressure bar: [Specify maximum pressure in bar]
- Operating Pressure: [Specify operating pressure range or value]
The Operation Theory of Modulating Control Valve
The operation theory of Modulating Control Valves involves adjusting fluid flow to maintain desired conditions in a system. These valves, like the thermo control valve Subaru and air volume control valve, modulate flow based on external signals. In the case of thermo control valves, they regulate coolant flow in automotive engines to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Air volume control valves manage airflow in HVAC systems to ensure proper ventilation. By modulating the valve’s position, flow rates are adjusted, allowing for precise control over temperature, pressure, or airflow, depending on the application. This versatile functionality makes Modulating Control Valves indispensable in various industrial and automotive systems.
The Parameters Table of Modulating Control Valve
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Valve Type | Modulating Control Valve |
| Ball Material | Material of the ball (e.g., stainless steel) |
| Attachment Type | Type of attachment (e.g., flanged, threaded) |
| Thread Standard | Standard for threads (e.g., NPT, BSP) |
| Thread Size | Size of threads (e.g., 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch) |
| Body Material | Material of the valve body (e.g., carbon steel, PVC) |
| Safe for Use With | Compatible fluid or application |
| Handle Type | Type of handle (e.g., lever, knob) |
| Handle Material | Material of the handle (e.g., plastic, aluminum) |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | Maximum pressure in psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | Maximum pressure in bar |
| Operating Pressure | Operating pressure range or value |
