Hydraulic Valve Body
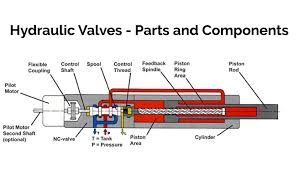
The Application of Hydraulic Valve
Introducing Hydraulic Valve: Hydraulic systems rely on various valves to control fluid flow and pressure. Among them, hydraulic pressure relief valve ensures system safety by releasing excess pressure. Hydraulic solenoid valve offers precise control, directing fluid flow based on electrical signals. Hydraulic check valve permits fluid flow in one direction, preventing backflow. Additionally, hydraulic diverter valve redirects fluid flow to different paths as needed. These valves play crucial roles in diverse hydraulic applications, from heavy machinery to industrial equipment, ensuring smooth operation and system integrity, especially in scenarios requiring precise pressure control like in a 3 bar Hydraulic Valve system.
What Is Hydraulic Valve?
Hydraulic Valve refers to a vital component in hydraulic systems responsible for controlling the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid. These valves come in various types, such as hydraulic pressure relief valve, hydraulic solenoid valve, hydraulic check valve, and hydraulic diverter valve, each serving specific functions to ensure the proper operation and safety of hydraulic machinery and systems. They play a crucial role in regulating fluid flow direction, pressure levels, and overall system performance in a wide range of applications across industries like manufacturing, construction, and automotive.
How Does Hydraulic Valve work?
Hydraulic valves operate based on the principles of fluid dynamics and control. When hydraulic fluid flows through the system, the hydraulic valve regulates its direction, pressure, and flow rate. Hydraulic pressure relief valves release excess pressure to prevent damage to the system, while hydraulic solenoid valves control fluid flow based on electrical signals. Hydraulic check valves allow fluid flow in one direction only, preventing backflow, and hydraulic diverter valves redirect fluid to different paths as needed. These valves play critical roles in maintaining the efficiency, safety, and functionality of hydraulic systems across various applications.
Features of Hydraulic Valve
- Versatility: Hydraulic valves come in various types, including pressure relief, solenoid, check, and diverter valves, catering to diverse application needs.
- Precision Control: They offer precise control over fluid flow, pressure, and direction, ensuring efficient operation and system performance.
- Safety: Hydraulic valves, such as pressure relief valves, prioritize system safety by preventing over-pressurization and potential damage.
- Durability: Constructed from robust materials like stainless steel and brass, hydraulic valves are designed to withstand high pressures and harsh environments.
- Reliability: With their sturdy construction and reliable operation, hydraulic valves ensure consistent performance, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Customization: Many hydraulic valves can be customized with specific features and specifications to suit unique application requirements.
- Ease of Installation: Designed for straightforward installation and integration into hydraulic systems, these valves streamline setup and maintenance processes.
Advantages of Hydraulic Valve
- Precise Control: Hydraulic valves offer precise control over fluid flow, pressure, and direction, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in hydraulic systems.
- Safety: They prioritize system safety by preventing over-pressurization and potential damage, especially with features like pressure relief valves.
- Versatility: Hydraulic valves come in various types to cater to diverse application needs, from pressure relief to solenoid, check, and diverter valves.
- Reliability: With sturdy construction and reliable operation, hydraulic valves ensure consistent performance, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Durability: Constructed from robust materials like stainless steel and brass, hydraulic valves are designed to withstand high pressures and harsh environmental conditions, enhancing longevity and reliability.
- Customization: Many hydraulic valves can be customized with specific features and specifications to suit unique application requirements, providing flexibility and adaptability.
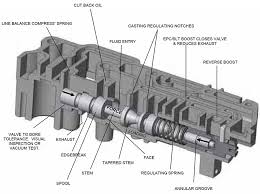
The Specifications of Hydraulic Valve
| Specification | Hydraulic Valve |
|---|---|
| Type | Pressure Relief, Solenoid, Check, Diverter |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, PTFE, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, etc. |
| Thread Standard | ANSI, DIN, BS, JIS, etc. |
| Thread Size | Various sizes available |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Cast Iron, etc. |
| Safe for Use With | Hydraulic Fluids, Oils, Water, etc. |
| Handle Type | Lever, Knob, Wheel, etc. |
| Handle Material | Steel, Aluminum, Plastic, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Specific value (psi) |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Specific value (bar) |
| Operating Pressure | Varies based on specifications |
The Parameter of Hydraulic Valve
- Type: Hydraulic valves are available in various types, including pressure relief, solenoid, check, and diverter valves, each serving specific functions in hydraulic systems.
- Ball Material: The ball material of hydraulic valves can vary and may include options like stainless steel, brass, PTFE, and other durable materials depending on the application requirements.
- Attachment Type: Hydraulic valves come with different attachment types such as flanged, threaded, welded, etc., providing flexibility in installation and integration into hydraulic systems.
- Thread Standard: They conform to various thread standards like ANSI, DIN, BS, JIS, etc., ensuring compatibility with different piping systems.
- Thread Size: Hydraulic valves are available in various thread sizes to accommodate different piping requirements and specifications.
- Body Material: The body material of hydraulic valves may include stainless steel, brass, cast iron, etc., chosen based on factors like pressure rating, fluid compatibility, and environmental conditions.
- Safe for Use With: Hydraulic valves are suitable for use with hydraulic fluids, oils, water, and other compatible fluids commonly used in hydraulic systems.
- Handle Type: They come with different handle types such as lever, knob, wheel, etc., facilitating manual operation and control of the valve.
- Handle Material: The handle material may include options like steel, aluminum, plastic, etc., chosen for durability and ease of operation.
- Maximum Working Pressure: Hydraulic valves have a specific maximum working pressure rating in psi and bar, indicating the maximum pressure they can withstand while in operation.
- Operating Pressure: The operating pressure of hydraulic valves varies based on specific model and application requirements, ensuring optimal performance within specified pressure ranges.
The Operation Theory of Hydraulic Valve
- Hydraulic Pressure Reducing Valve: This type regulates and reduces the hydraulic pressure in a system by diverting excess pressure to a secondary circuit or by restricting the flow of hydraulic fluid.
- Hydraulic Relief Valve: Designed to safeguard hydraulic systems from over-pressurization, the hydraulic relief valve automatically opens to release excess pressure when it exceeds a predetermined limit, preventing damage to system components.
The Parameters Table of Hydraulic Valve
| Parameter | Hydraulic Valve |
|---|---|
| Type | Pressure Relief, Solenoid, Check, Diverter |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, PTFE, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, etc. |
| Thread Standard | ANSI, DIN, BS, JIS, etc. |
| Thread Size | Various sizes available |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Cast Iron, etc. |
| Safe for Use With | Hydraulic Fluids, Oils, Water, etc. |
| Handle Type | Lever, Knob, Wheel, etc. |
| Handle Material | Steel, Aluminum, Plastic, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Specific value (psi) |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Specific value (bar) |
| Operating Pressure | Varies based on specifications |
