Spirax Sarco Pressure Reducing Valves DP17
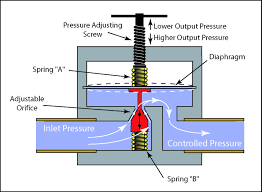
The Application of Pressure Reducing Valves
When it comes to controlling pressure in various systems, Pressure Reducing Valves play a crucial role. Whether it’s managing water flow in a ball valve for pressure washer, regulating air pressure in air compressor Pressure Reducing Valves, or ensuring safety with a 3/4 pressure relief valve, these valves are indispensable. Among the leading brands, Cameron stands out for its quality and reliability in this field. Pressure Reducing Valves work by automatically adjusting to maintain a consistent pressure level downstream, preventing damage and ensuring optimal performance. From industrial applications to household plumbing, these valves offer precision and efficiency, making them essential components in a wide range of systems.
spirax sarco prv
spirax sarco prv 25p
What Are The Types Of Pressure Reducing Valves?
- Direct-Acting Pressure Reducing Valve: This type operates using a diaphragm or piston directly exposed to the downstream pressure. Changes in downstream pressure directly affect the valve’s position, allowing for quick and accurate pressure regulation.
- Pilot-Operated Pressure Reducing Valve: In this type, a pilot valve controls the main valve’s position based on signals from the downstream pressure. Pilot-operated valves are often used for high-pressure applications or where precise control is required.
- Proportional Pressure Reducing Valve: These valves adjust the pressure proportionally to changes in the input signal, making them suitable for applications where precise pressure control is essential, such as in hydraulic systems.
- Balanced-Seat Pressure Reducing Valve: Balanced-seat valves use a balanced design to maintain consistent performance even with varying inlet pressures. They are suitable for applications with fluctuating upstream pressures.
- Temperature-Compensated Pressure Reducing Valve: These valves incorporate temperature sensors to adjust the pressure based on changes in temperature, ensuring stable pressure regulation despite temperature variations.
- Pressure Relief Valve: While primarily used for overpressure protection, pressure relief valves can also function as pressure reducing valves by diverting excess pressure when needed, thus maintaining a safe operating pressure.
What Is Pressure Reducing Valves?
Pressure Reducing Valves are mechanical devices designed to regulate and control the pressure of fluid or gas in a system. They work by reducing the incoming pressure from the supply line to a lower, predetermined level suitable for downstream applications. These valves are crucial in maintaining safe operating conditions, preventing damage to equipment, and ensuring optimal performance. Pressure Reducing Valves find applications in various industries, including plumbing, HVAC systems, industrial processes, and pneumatic systems, where precise pressure control is essential for efficiency and safety.
How Does Pressure Reducing Valves work?
Pressure Reducing Valves work by automatically adjusting the flow of fluid or gas to maintain a consistent pressure downstream. When the upstream pressure exceeds the set limit, the valve opens, allowing the excess pressure to escape, thus reducing the pressure in the system. Conversely, when the pressure drops below the set limit, the valve closes to restrict the flow and maintain the desired pressure level. This continuous adjustment ensures stable pressure regulation and protects downstream equipment from damage.
Features of Pressure Reducing Valves
- Versatility: They are versatile and compatible with various fluids and gases, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
- Pressure Relief: Some Pressure Reducing Valves also function as pressure relief valves, diverting excess pressure to protect downstream equipment from damage.
- Ease of Installation: Designed for easy installation and maintenance, these valves feature simple designs and accessible components, reducing downtime and labor costs.
- Compact Design: Many Pressure Reducing Valves come in compact sizes, allowing for space-saving installation in tight or confined spaces.
- Compliance: They meet industry standards and regulations for safety and performance, providing peace of mind to users.
- Monitoring Capabilities: Some advanced models feature monitoring and control options, allowing users to remotely monitor and adjust pressure settings for optimal operation.
Advantages of Pressure Reducing Valves
- Prevent Damage: By reducing the pressure to a safe and manageable level, these valves prevent damage to downstream equipment and piping caused by excessive pressure.
- Energy Efficiency: Pressure Reducing Valves help conserve energy by reducing the amount of energy required to operate equipment and systems at lower pressures.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: By maintaining optimal pressure levels, these valves contribute to extending the lifespan of equipment and components, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
- Safety: They enhance safety by preventing pressure-related accidents and failures, ensuring a safe working environment for personnel and minimizing the risk of system failures.
- Regulation of Flow: These valves not only control pressure but also regulate the flow of fluid or gas, ensuring consistent and reliable operation of systems and processes.
- Versatility: Pressure Reducing Valves are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications and industries, from industrial processes to residential plumbing systems.
- Cost-Effectiveness: They offer a cost-effective solution for managing pressure, reducing the need for expensive equipment repairs or replacements due to pressure-related issues.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Many Pressure Reducing Valves are designed for easy installation and maintenance, saving time and labor costs for system operators.
- Compatibility: These valves are compatible with various fluids and gases, making them suitable for diverse applications without compromising performance.
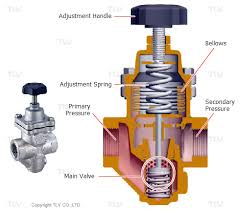
The Specifications of Pressure Reducing Valves
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Pressure Reducing Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel |
| Attachment Type | Threaded |
| Thread Standard | NPT (National Pipe Thread) |
| Thread Size | 3/4 inch |
| Body Material | Brass |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Air, Gas |
| Handle Type | Lever |
| Handle Material | Zinc Alloy |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | 150 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | 10.34 bar |
| Operating Pressure | 10-90 psi |
The Parameter of Pressure Reducing Valves
- Type: Pressure Reducing Valve
- Ball Material: Stainless Steel
- Attachment Type: Threaded
- Thread Standard: NPT (National Pipe Thread)
- Thread Size: 3/4 inch
- Body Material: Brass
- Safe for Use With: Water, Air, Gas
- Handle Type: Lever
- Handle Material: Zinc Alloy
- Maximum Working Pressure (psi): 150 psi
- Maximum Working Pressure (bar): 10.34 bar
- Operating Pressure: 10-90 psi
The Operation Theory of Pressure Reducing Valves
- Pressure Reducing Valves operation theory: Pressure Reducing Valves regulate and control the pressure of fluids or gases in a system. They operate based on the principle of balancing forces to maintain a constant downstream pressure. When the upstream pressure exceeds the set limit, the valve opens, allowing the excess pressure to escape. Conversely, when the pressure drops below the set limit, the valve closes to restrict the flow and maintain the desired pressure level. This operation is symbolized by the Pressure Reducing Valves symbol, indicating the device’s function in maintaining pressure stability.
- 3/4 Pressure Reducing Valves: This refers to Pressure Reducing Valves with a thread size of 3/4 inch, suitable for specific applications requiring precise pressure control within a certain range.
- Adjustable Pressure Reducing Valves: Unlike fixed-pressure valves, adjustable Pressure Reducing Valves allow users to set and regulate the desired outlet pressure according to specific application requirements. This adjustability adds flexibility and customization to pressure control systems, ensuring optimal performance in various settings.

