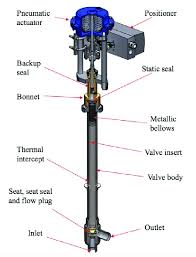
Why Cryogenic Valves Have Long Stem

The Application of Cryogenic Valves
Cameron, a leader in industrial solutions, offers premium cryogenic valves designed for extreme low-temperature applications. These valves, including cryogenic safety valves and cryogenic ball valve designs like Worcester cryogenic ball valves, ensure reliable performance in cryogenic environments. With specialized materials and precision engineering, they maintain integrity and safety even in harsh conditions. Cryogenic globe valves, another essential variant, provide efficient flow control and sealing capabilities. Engineered to withstand ultra-low temperatures, they play a crucial role in industries such as LNG, petrochemical, and aerospace. Cameron’s commitment to quality and innovation ensures that its cryogenic valves meet stringent industry standards, offering unmatched reliability and performance in critical cryogenic applications.
Why Cryogenic Valves Have Long Stem
- Temperature Control: The long stem helps keep the operating components of the valve, such as the handle or actuator, at a safe distance from the extremely cold temperatures of cryogenic fluids. This prevents freezing or damage to the valve’s operational mechanisms.
- Insulation: By extending the stem away from the cold environment, the valve’s stem can be insulated more effectively. Insulation helps prevent the stem from becoming brittle or seizing up due to the extreme cold, ensuring smooth operation even at low temperatures.
- Accessibility: Cryogenic valves are often installed in environments with limited access or in systems where manual operation is necessary. The long stem provides easier access to the valve for operation, maintenance, and repairs, even in challenging or confined spaces.
- Safety: In some cases, the long stem serves as a visual indicator, allowing operators to see the position of the valve from a distance. This enhances safety by providing clear visibility of the valve’s status, particularly in hazardous environments.
What Is Cryogenic Valves?
Cryogenic valves are specialized valves designed to handle extremely low temperatures encountered in cryogenic applications. They ensure the safe and reliable control of fluids such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), liquid oxygen, and liquid nitrogen. These valves are constructed with materials capable of withstanding the severe cold and are engineered to maintain tight seals and efficient operation even in the harsh conditions of cryogenic environments.
How Does Cryogenic Valves work?
Cryogenic valves operate by utilizing specialized materials and designs to withstand the extreme cold of cryogenic fluids. They feature tight seals and precision mechanisms to control the flow of liquefied gases such as LNG, liquid oxygen, and liquid nitrogen. When the valve is opened, it allows the controlled release or passage of cryogenic fluids, while when closed, it forms a tight seal to prevent leakage or loss of the valuable cryogenic substances. These valves ensure safe and efficient handling of extremely low-temperature fluids in various industrial applications.
Features of Cryogenic Valves
- Specialized Materials: Constructed with materials such as stainless steel or brass, ensuring compatibility with extreme low temperatures.
- Extended Stem: Longer stems facilitate operation and insulation, keeping critical components away from the cold and reducing the risk of freezing.
- Low-Temperature Seals: Employ advanced sealing materials like PTFE (Teflon) or elastomers to maintain tight seals even in cryogenic conditions.
- Precision Engineering: Designed with precision to ensure smooth operation and reliability, critical in handling cryogenic fluids.
- Leak Prevention: Incorporate features like double sealing to minimize the risk of leakage, crucial for safety and efficiency.
- Safety Standards: Manufactured to comply with stringent safety standards to guarantee safe handling of cryogenic substances.
- Adaptability: Available in various configurations such as ball valves, globe valves, and gate valves to suit different applications.
- Temperature Monitoring: Some models feature temperature indicators or sensors to monitor the operating conditions and prevent issues related to extreme temperatures.
- Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to corrosion from cryogenic fluids, ensuring long-term durability and performance.
Advantages of Cryogenic Valves
- Extreme Temperature Handling: Engineered to withstand extremely low temperatures encountered in cryogenic applications, ensuring reliable operation even in harsh conditions.
- Tight Sealing: Designed with specialized materials and seals to maintain tight shut-off and prevent leakage of cryogenic fluids, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Precision Control: Offer precise control over the flow of cryogenic fluids, allowing for accurate regulation and management of processes.
- Versatility: Available in various types such as ball valves, globe valves, and gate valves, catering to a wide range of cryogenic applications and requirements.
- Safety Features: Incorporate safety features such as extended stems for insulation and temperature monitoring to prevent issues associated with cryogenic temperatures.
- Durability: Constructed with high-quality materials that withstand the extreme conditions of cryogenic environments, ensuring long-term durability and reliability.
- Compliance: Manufactured to meet industry standards and regulations, providing assurance of quality, safety, and performance.
- Minimal Maintenance: Require minimal maintenance due to their robust construction and specialized design, reducing downtime and operational costs.
The Specifications of Cryogenic Valves
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Cryogenic Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded |
| Thread Standard | ASME B1.20.1, DIN, ISO |
| Thread Size | 1/2 inch to 2 inches (for threaded), 2 inches to 24 inches (for flanged) |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Carbon Steel, Aluminum |
| Safe for Use With | Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), Liquid Oxygen, Liquid Nitrogen, Helium, Hydrogen |
| Handle Type | Handwheel, Gear Operator, Actuator |
| Handle Material | Stainless Steel, Aluminum Alloy, Plastic |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | Up to 1500 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | Up to 103.4 bar |
| Operating Pressure | 10 psi to 1500 psi (0.7 bar to 103.4 bar) |
The Parameter of Cryogenic Valves
- Type: Cryogenic Valve
- Ball Material Options: Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze
- Attachment Types Available: Flanged, Threaded
- Thread Standard: ASME B1.20.1, DIN, ISO
- Thread Size Range: 1/2 inch to 2 inches (for threaded), 2 inches to 24 inches (for flanged)
- Body Material Choices: Stainless Steel, Brass, Carbon Steel, Aluminum
- Safe for Use With: Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), Liquid Oxygen, Liquid Nitrogen, Helium, Hydrogen
- Handle Types: Handwheel, Gear Operator, Actuator
- Handle Material Options: Stainless Steel, Aluminum Alloy, Plastic
- Maximum Working Pressure (psi): Up to 1500 psi
- Maximum Working Pressure (bar): Up to 103.4 bar
- Operating Pressure Range: From 10 psi to 1500 psi (0.7 bar to 103.4 bar)
The Operation Theory of Cryogenic Valves
The operation theory of cryogenic valves, including cryogenic ball valves and cryogenic control valves, revolves around their ability to function effectively in extreme low-temperature environments. These valves employ specialized materials and designs to withstand the cold temperatures encountered in cryogenic applications. When the valve is opened, it allows the controlled flow of cryogenic fluids such as liquefied natural gas (LNG) or liquid nitrogen. This is achieved through the movement of the valve’s internal components, such as the ball or control mechanism, which are designed to maintain tight seals and efficient flow control even at cryogenic temperatures. When the valve is closed, it forms a tight seal to prevent leakage or loss of the valuable cryogenic substances. Overall, the operation theory of cryogenic valves ensures safe and efficient handling of extremely low-temperature fluids in various industrial applications.
The Parameters Table of Cryogenic Valves
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Cryogenic Valve |
| Ball Material Options | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze |
| Stem Material Options | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Seat Material Options | PTFE (Teflon), Peek, PCTFE, Graphite |
| Body Material Options | Stainless Steel, Brass, Carbon Steel, Aluminum |
| Bonnet Material Options | Stainless Steel, Brass, Carbon Steel, Aluminum |
| Seal Material Options | PTFE (Teflon), NBR (Nitrile), Viton, EPDM |
| Handle Material Options | Stainless Steel, Aluminum Alloy, Plastic |
| Bolting Material Options | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Flange Material Options | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Operating Mechanism | Manual (Handwheel), Gear Operator, Actuator |
| Operating Temperature | -196°C to 150°C (-320°F to 302°F) |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Up to 1500 psi |
| Compliance Standards | API 6D, ISO 15848, ASME B16.34, BS 6364, EN 1626 |
