Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve

The Application of Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve
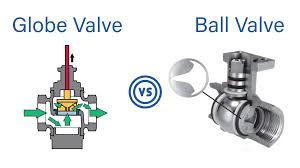
In comparing Globe Valve and Ball Valve, both are essential components in fluid control systems. Rotork Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve exemplifies this distinction. While globe valves regulate flow using a linear motion of a plug against the seat, ball valves employ a rotating ball to control flow. Globe valves are ideal for throttling applications, offering precise flow control, while ball valves, like the Cameron T31 ball valve, are better suited for on/off service due to their quick operation. Additionally, globe valves exhibit higher pressure drop compared to ball valves, making them less efficient for high-flow applications. Choosing between a 1 2 globe valve and a ball valve depends on factors such as flow rate, pressure, and application requirements.
What Is Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve?
A Globe Valve manages fluid flow by moving a plug linearly, offering precise control. Conversely, a Ball Valve regulates flow with a rotating ball, typically for quick on/off service and less precise control compared to a globe valve.
How Does Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve work?
Globe valves control fluid flow by moving a plug against a seat to regulate flow. In contrast, ball valves use a rotating ball to open or close the passage, allowing or stopping the flow of fluid.
Features of Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve
- Globe Valve:
- Precise Control: Offers precise regulation of fluid flow, making it suitable for throttling applications.
- Linear Motion: Operates with a linear motion of the plug against the seat, allowing for fine adjustments.
- High Pressure Drop: Typically exhibits a higher pressure drop compared to ball valves.
- Suitable for High Temperatures: Can withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions due to its robust design.
- Commonly Used in Industries: Widely used in industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing.
- Ball Valve:
- Quick Operation: Operates quickly with a rotating ball mechanism, making it ideal for on/off service.
- Less Precise Control: Provides less precise flow control compared to globe valves.
- Low Pressure Drop: Typically experiences a lower pressure drop, ensuring efficient flow in high-flow applications.
- Compact Design: Features a compact and lightweight design, making it suitable for space-constrained installations.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Advantages of Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve
- Advantages of Globe Valve:
- Precise Control: Globe valves offer precise control over fluid flow, making them suitable for throttling applications where accurate regulation is required.
- Versatility: They can handle a wide range of flow rates and pressures, making them versatile in various industries.
- Reliability: Globe valves have a robust design and are known for their durability and reliability in demanding environments.
- Suitability for High Temperatures: They are suitable for high-temperature applications, such as steam systems, due to their sturdy construction and materials.
- Advantages of Ball Valve:
- Quick Operation: Ball valves operate quickly and can be opened or closed rapidly, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent on/off operation.
- Low Maintenance: They have a simple design with fewer moving parts, resulting in lower maintenance requirements compared to globe valves.
- Low Pressure Drop: Ball valves typically experience minimal pressure drop across the valve, ensuring efficient flow even in high-flow applications.
- Compact Design: Their compact size and lightweight construction make them easy to install and suitable for space-constrained installations.
The Specifications of Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve
| Specification | Globe Valve | Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Globe Valve | Ball Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, or Bronze | Stainless Steel, Brass, or Chrome-plated Brass |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, or Welded | Threaded, Flanged, or Socket Welded |
| Thread Standard | ANSI, BSPT, NPT, DIN, or JIS | ANSI, BSPT, NPT, DIN, or JIS |
| Thread Size | Typically 1/2 inch to 24 inches | Typically 1/4 inch to 4 inches |
| Body Material | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, or Stainless Steel | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, or Stainless Steel |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Steam, Oil, Gas, or Other Fluids | Water, Oil, Gas, or Other Fluids |
| Handle Type | Handwheel, Gear Operated, or Actuator | Lever, Handle, or Actuator |
| Handle Material | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Stainless Steel, or Aluminum | Stainless Steel, Aluminum, or Plastic |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | Typically up to 2500 psi | Typically up to 1000 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | Typically up to 172 bar | Typically up to 69 bar |
| Operating Pressure | Range: 5-200 psi (0.3-14 bar) or Adjustable | Typically 10-100 psi (0.7-7 bar) or Adjustable |
The Parameter of Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve
- Type:
- Globe Valve: Designed with a globe-shaped body and a plug that moves linearly to regulate flow.
- Ball Valve: Features a spherical closure element (ball) that rotates to open or close the flow passage.
- Ball Material:
- Globe Valve: The plug material varies, commonly stainless steel, brass, or bronze.
- Ball Valve: The ball material typically consists of stainless steel, brass, or chrome-plated brass.
- Attachment Type:
- Globe Valve: Available in flanged, threaded, or welded configurations.
- Ball Valve: Offered in threaded, flanged, or socket welded options.
- Thread Standard:
- Both valves are available in various thread standards, including ANSI, BSPT, NPT, DIN, or JIS.
- Thread Size:
- Globe Valve: Typically ranges from 1/2 inch to 24 inches.
- Ball Valve: Generally ranges from 1/4 inch to 4 inches.
- Body Material:
- Globe Valve: Constructed from cast iron, ductile iron, carbon steel, or stainless steel.
- Ball Valve: Made of cast iron, ductile iron, carbon steel, or stainless steel.
- Safe for Use With:
- Both valves are suitable for use with water, steam, oil, gas, or other fluids.
- Handle Type:
- Globe Valve: Equipped with a handwheel, gear-operated mechanism, or actuator.
- Ball Valve: Comes with a lever, handle, or actuator for operation.
- Handle Material:
- Globe Valve: Handles are typically made of cast iron, ductile iron, stainless steel, or aluminum.
- Ball Valve: Handles are commonly constructed from stainless steel, aluminum, or plastic.
- Maximum Working Pressure:
- Globe Valve: Typically handles up to 2500 psi (172 bar).
- Ball Valve: Usually operates at pressures up to 1000 psi (69 bar).
- Operating Pressure:
- Globe Valve: Operates within a range of 5-200 psi (0.3-14 bar) or adjustable.
- Ball Valve: Typically operates between 10-100 psi (0.7-7 bar) or adjustable.
The Operation Theory of Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve
- Globe Valve:
- Operation: Globe valves regulate flow by moving a plug in a linear motion against the flow path. This movement restricts or allows the flow of fluid through the valve.
- Functionality: As the plug moves, it either opens or closes the flow passage. The degree of opening determines the flow rate through the valve, allowing for precise control of fluid flow.
- PVC Globe Valve: In PVC globe valves, the operation remains the same, but the materials used are PVC (polyvinyl chloride) instead of metal, making them suitable for corrosive environments.
- Ball Valve:
- Operation: Ball valves control flow using a spherical closure element (the ball) that rotates within the valve body. When the ball’s bore aligns with the flow path, fluid can pass through the valve.
- Functionality: Rotating the ball 90 degrees either opens or closes the valve completely, providing quick on/off control of fluid flow.
- Ball Valve Design: The design of a ball valve allows for minimal flow resistance and pressure drop when fully open, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid shut-off or precise control.
The Parameters Table of Globe Valve Vs Ball Valve
| Parameter | Globe Valve | Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Globe Valve | Ball Valve |
| Material | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, PVC (for certain applications) | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded | Threaded, Flanged, Socket Welded |
| Thread Standard | ANSI, BSPT, NPT, DIN, JIS | ANSI, BSPT, NPT, DIN, JIS |
| Thread Size | Typically 1/2 inch to 24 inches | Typically 1/4 inch to 4 inches |
| Body Material | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, PVC (for certain applications) | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Steam, Oil, Gas, Various Fluids | Water, Oil, Gas, Various Fluids |
| Handle Type | Handwheel, Gear Operated, Actuator | Lever, Handle, Actuator |
| Handle Material | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Stainless Steel, Aluminum | Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Plastic |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Typically up to 2500 psi (172 bar) | Typically up to 1000 psi (69 bar) |
| Operating Pressure | Range: 5-200 psi (0.3-14 bar), Adjustable | Typically 10-100 psi (0.7-7 bar), Adjustable |
