Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve
The Application of Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve
In the realm of valve selection, the debate between plug vs ball valve has long persisted, with each offering distinct advantages. While ball valve vs plug valve discussions often center on factors like flow control and sealing capabilities, the choice ultimately hinges on specific application requirements. For instance, eccentric plug valve vs ball valve comparisons highlight the former’s superior sealing abilities, making it a preferred choice for applications demanding tight shut-off, such as gas transmission. Conversely, plug valve vs ball valve for gas applications might favor the latter’s streamlined design and ease of operation. Whether it’s a 3 bar Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve scenario, careful consideration of factors like pressure, flow rate, and media compatibility is crucial in making the optimal valve selection.
plug valves vs ball valves
cameron butterfly valve
knife gate valve symbol
pressure control valve symbol
globe valve vs plug valve
plug valve vs globe valve
plug valve symbol
What Is Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve?
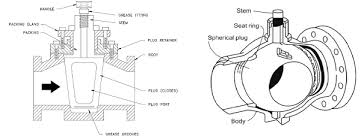
Plug valve vs ball valve is a comparison often encountered in valve selection. The primary difference lies in their internal mechanisms. A plug valve utilizes a cylindrical or tapered plug to control flow, while a ball valve employs a spherical ball with a hole through it. These valves offer distinct advantages based on factors like sealing capabilities, flow control, and ease of operation. Understanding their unique features is crucial in selecting the most suitable valve for specific applications.
How Does Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve work?
Plug valve vs ball valve operate differently based on their internal mechanisms. In a plug valve, a cylindrical or tapered plug rotates within the valve body to control flow. Conversely, in a ball valve, a spherical ball with a hole through it rotates to open or close the flow path. Each valve offers distinct advantages in flow control and sealing capabilities, catering to various application requirements.
Features of Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve
- Sealing Capability: Plug valves are known for their excellent sealing capabilities, especially in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, thanks to the tight fit of the plug against the valve body. Ball valves, on the other hand, offer reliable sealing due to the tight closure of the ball against the valve seat.
- Flow Control: Ball valves provide precise flow control with a quarter-turn operation, making them ideal for applications requiring quick shut-off or modulation. Plug valves, with their cylindrical or tapered plug design, offer versatile flow control, including throttling and isolation.
- Maintenance: Plug valves typically have fewer parts and a simpler design, making them easier to maintain and repair compared to ball valves, which may require more frequent maintenance due to the complexity of their internal components.
- Durability: Both plug valves and ball valves are known for their durability and resistance to corrosion, with options available in various materials such as stainless steel, brass, and cast iron, ensuring longevity and reliability in harsh environments.
Advantages of Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve
- Sealing Performance: Plug valves generally offer better sealing performance than ball valves, particularly in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, due to the tight fit of the plug against the valve body.
- Flow Control Flexibility: Plug valves provide greater flexibility in flow control, allowing for precise throttling and isolation, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Simple Design: Plug valves often have a simpler design with fewer moving parts compared to ball valves, resulting in easier maintenance and lower risk of failure.
- Reliability: Both types of valves are known for their reliability, but plug valves may offer slightly higher reliability in certain applications due to their robust construction and sealing capabilities.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Depending on the application, plug valves may be more cost-effective than ball valves, especially for applications requiring high-pressure or high-temperature performance.

The Specifications of Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve
| Specification | Plug Valve | Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Plug Valve | Ball Valve |
| Ball Material | Brass, Stainless Steel, PTFE, etc. | Brass, Stainless Steel, PTFE, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, etc. | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, etc. |
| Thread Standard | ANSI, DIN, BS, JIS, etc. | ANSI, DIN, BS, JIS, etc. |
| Thread Size | Various sizes available | Various sizes available |
| Body Material | Brass, Stainless Steel, Cast Iron, etc. | Brass, Stainless Steel, Cast Iron, etc. |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Air, Gas, Steam, etc. | Water, Air, Gas, Steam, etc. |
| Handle Type | Lever, Knob, Wheel, etc. | Lever, Knob, Wheel, etc. |
| Handle Material | Steel, Aluminum, Plastic, etc. | Steel, Aluminum, Plastic, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Up to specific value (psi) | Up to specific value (psi) |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Up to specific value (bar) | Up to specific value (bar) |
| Operating Pressure | Varies based on specifications | Varies based on specifications |
The Parameter of Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve
- Type:
- Plug Valve: Features a cylindrical or tapered plug to control flow.
- Ball Valve: Utilizes a spherical ball with a hole through it to regulate flow.
- Ball Material:
- Plug Valve: Can be made of brass, stainless steel, PTFE, etc.
- Ball Valve: Options include brass, stainless steel, PTFE, etc.
- Attachment Type:
- Plug Valve: Available in various attachment types such as flanged, threaded, welded, etc.
- Ball Valve: Also offered in attachment types like flanged, threaded, welded, etc.
- Thread Standard:
- Plug Valve: Can conform to standards like ANSI, DIN, BS, JIS, etc.
- Ball Valve: Similarly conforms to standards such as ANSI, DIN, BS, JIS, etc.
- Thread Size:
- Plug Valve: Comes in various sizes to fit different piping requirements.
- Ball Valve: Also available in various sizes to accommodate different piping systems.
- Body Material:
- Plug Valve: Constructed from materials like brass, stainless steel, cast iron, etc.
- Ball Valve: Similarly constructed from materials such as brass, stainless steel, cast iron, etc.
- Safe for Use With:
- Plug Valve: Suitable for use with water, air, gas, steam, etc.
- Ball Valve: Also suitable for use with water, air, gas, steam, etc.
- Handle Type:
- Plug Valve: Offered with different handle types such as lever, knob, wheel, etc.
- Ball Valve: Similarly offered with handle types like lever, knob, wheel, etc.
- Handle Material:
- Plug Valve: Handles can be made of materials like steel, aluminum, plastic, etc.
- Ball Valve: Handles can also be made of materials such as steel, aluminum, plastic, etc.
- Maximum Working Pressure:
- Plug Valve: Can handle pressures up to a specific value in psi/bar.
- Ball Valve: Can also handle pressures up to a specific value in psi/bar.
- Operating Pressure:
- Plug Valve: Operating pressure varies based on specific model and application requirements.
- Ball Valve: Operating pressure similarly varies based on specific model and application requirements.
The Operation Theory of Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve
- Plug Valves: Utilize a cylindrical or tapered plug to control flow. When the plug rotates, it either opens or obstructs the flow path, regulating the flow of fluids or gases. The sealing surface of the plug ensures tight shut-off, making it ideal for applications requiring reliable isolation.
- Ball Valves: Operate by rotating a spherical ball with a hole through it to control flow. When the ball is turned perpendicular to the flow direction, it blocks flow; when parallel, it allows flow. The quarter-turn operation of ball valves offers quick shut-off and precise control, making them suitable for various applications.
Considering the advantages of ball valve vs plug valve, ball valves often excel in providing precise flow control, ease of operation, and quick shut-off, especially in applications where frequent operation is required or space is limited. However, plug valves are preferred for their robust sealing capabilities, making them suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications where tight shut-off is crucial.
The Parameters Table of Plug Valve Vs Ball Valve
| Parameter | Plug Valve | Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Plug Valve | Ball Valve |
| Material | Brass, Stainless Steel, PTFE, etc. | Brass, Stainless Steel, PTFE, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, etc. | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, etc. |
| Thread Standard | ANSI, DIN, BS, JIS, etc. | ANSI, DIN, BS, JIS, etc. |
| Thread Size | Various sizes available | Various sizes available |
| Body Material | Brass, Stainless Steel, Cast Iron, etc. | Brass, Stainless Steel, Cast Iron, etc. |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Air, Gas, Steam, etc. | Water, Air, Gas, Steam, etc. |
| Handle Type | Lever, Knob, Wheel, etc. | Lever, Knob, Wheel, etc. |
| Handle Material | Steel, Aluminum, Plastic, etc. | Steel, Aluminum, Plastic, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Up to specific value (psi/bar) | Up to specific value (psi/bar) |
| Operating Pressure | Varies based on specifications | Varies based on specifications |
