High Pressure Check Valve 8 Inch 2500 LB
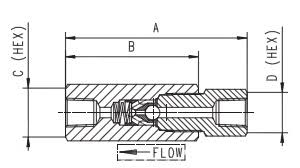
The Application of High Pressure Check Valve
The High Pressure Check Valve is crucial in controlling fluid flow in high-pressure systems. Widely used in various industries, these valves ensure unidirectional flow and prevent backflow. One prominent variant is the triple offset valve butterfly, known for its excellent sealing capabilities. Brands like Cameron offer superior quality and reliability in their valve products. Notably, the vanessa High Pressure Check Valve from Cameron exemplifies advanced engineering and durability, making it ideal for demanding applications. These valves are essential for maintaining system integrity and efficiency under high-pressure conditions.
What Are The Types Of High Pressure Check Valve?
- Swing Check Valve: Utilizes a swinging disc that opens with forward flow and closes against a seat when the flow reverses. Suitable for horizontal or vertical (flow upwards) installations.
- Lift Check Valve: Features a disc that moves up and down within a guide to allow flow in one direction and blocks it when the flow reverses. Ideal for high-pressure applications and horizontal installations.
- Ball Check Valve: Uses a spherical ball to block the flow when it reverses. It’s simple, effective, and often used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- Tilting Disc Check Valve: The disc tilts to allow flow and tilts back to close the flow when it reverses. This type offers a quick response and low-pressure drop.
- Dual Plate Check Valve (or Double Disc Check Valve): Consists of two spring-loaded half-circle discs that fold together upon forward flow and close upon reverse flow. This type is compact and provides a quick shutoff.
- Nozzle Check Valve: Designed with a streamlined disc to minimize pressure loss and ensure quick closure. It’s used in high-velocity applications and provides excellent dynamic response.
What Is High Pressure Check Valve?
A High Pressure Check Valve is a valve designed to allow fluid to flow in one direction while preventing backflow in high-pressure systems. It ensures unidirectional flow, protecting equipment from potential damage due to reverse flow. Types include swing, lift, ball, tilting disc, and dual plate check valves, each suitable for different applications and pressure conditions.
How to Select the Right High Pressure Check Valve?
To select the right High Pressure Check Valve, consider factors like the system’s pressure rating, flow rate, fluid type, and installation orientation. Evaluate different types (swing, lift, ball, tilting disc, dual plate) based on application needs. Choose a reliable brand like Cameron for quality and durability.
Features of High Pressure Check Valve
- Function: The key function of a High Pressure Check Valve is to prevent reverse flow of fluid.
- Design: These valves are designed with a spring-loaded disc or ball that moves in response to fluid pressure.
- Materials: High Pressure Check Valves are typically made of durable materials like stainless steel or alloy.
- Applications: They are commonly used in industries requiring high-pressure fluid control, such as oil & gas, aerospace, and hydraulic systems.
- Reliability: Known for their reliable performance, these valves offer long-term operation in demanding environments.
- Configurations: High Pressure Check Valves can come in various configurations like swing, lift, or piston style to suit different system requirements.
- Maintenance: Regular inspections and maintenance are important to ensure optimal performance and longevity of these valves.
Advantages and Disadvantages of High Pressure Check Valve
- Prevents Reverse Flow: Ensures that fluid flows in one direction, preventing backflow and potential damage to the system.
- Easy Installation: Typically easy to install in a pipeline system, requiring minimal additional components.
- Low Maintenance: Generally low maintenance requirements, reducing downtime and operational costs.
- Versatility: Can be used in a wide range of applications and industries where high-pressure fluid control is necessary.
- Compact Design: Occupies minimal space in the system, making it suitable for various installations.
Disadvantages of High Pressure Check Valve:
- Pressure Drop: May cause a slight pressure drop in the system due to the flow resistance of the valve.
- Potential Leakage: Improper installation or wear and tear over time can lead to leakage issues.
- Limited to One Direction: Restricts fluid flow to only one direction, which may not be suitable for all system configurations.
- Compatibility Issues: Selecting the wrong type of high-pressure check valve for a specific system can lead to inefficiencies.
- Cost: High-quality high-pressure check valves can be relatively expensive compared to standard valves.
The Specifications of High Pressure Check Valve
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Ball Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel 316 |
| Attachment Type | Threaded |
| Thread Standard | NPT |
| Thread Size | 1/2 inch |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel 316 |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas |
| Handle Type | Lever |
| Handle Material | Stainless Steel 316 |
| Maximum Working Pressure | 1000 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure | 69 bar |
| Operating Pressure | 0-1000 psi |
The Installation Steps for High Pressure Check Valve
- Ensure the pipeline is completely depressurized and drained before starting the installation.
- Locate the correct orientation of the check valve. The arrow on the valve body should point in the direction of the desired flow.
- Apply thread sealant, such as PTFE tape or pipe dope, to the valve’s threaded ends.
- Carefully thread the check valve into the pipeline, ensuring the threads are properly engaged. Use a wrench to tighten the valve, but do not over-tighten.
- Confirm that the valve is installed at the correct angle, with the arrow pointing in the desired flow direction.
- Slowly restore pressure to the system, checking for any leaks around the valve connections.
- Once the system is pressurized, operate the valve several times to ensure it is functioning properly and the piston/disc is moving freely.
- If any leaks are detected, depressurize the system and tighten the valve connections further.
- After successful installation and testing, the system is ready for normal operation, with the check valve providing reliable backflow prevention up to the maximum working pressure of 1000 psi (69 bar).
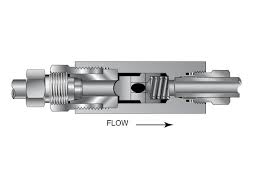
The Operation Theory of High Pressure Check Valve
Operation Theory of High Pressure Check Valve:
High pressure check valves are designed to allow flow in only one direction, preventing backflow and protecting downstream equipment. The valve contains a piston or disc that is spring-loaded to the closed position. When the upstream pressure overcomes the spring force, the piston/disc opens to allow forward flow. However, when the flow tries to reverse direction, the increased pressure pushes the piston/disc firmly against the valve seat, creating a tight seal and stopping backflow.
This simple yet robust design allows high pressure check valves to reliably maintain unidirectional flow, even in demanding applications with pressures up to 1000 psi (69 bar). The stainless steel construction and precision machining ensures long service life and minimal maintenance requirements.
ABZ High Pressure Check Valve:
One leading manufacturer of high pressure check valves is ABZ Valves. Their high pressure check valve line is engineered for rugged performance in oil & gas, petrochemical, and other industrial applications.
The ABZ high pressure check valve features a stainless steel 316 body and internal components for excellent corrosion resistance. It has a maximum working pressure of 1000 psi (69 bar) and is available in sizes from 1/2 inch to 2 inches. The valves can be configured with threaded, socket weld, or flanged end connections to suit the requirements of each project.
ABZ backs their high pressure check valves with a 5-year warranty, demonstrating the quality and reliability of their design. With a proven track record in the field, the ABZ high pressure check valve is a popular choice for engineers specifying backflow prevention in high-pressure systems.
